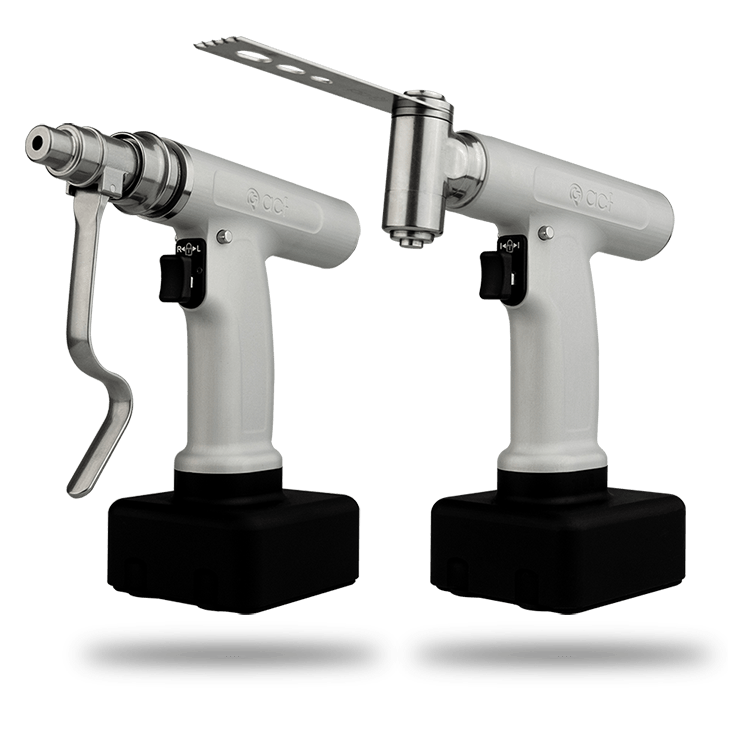
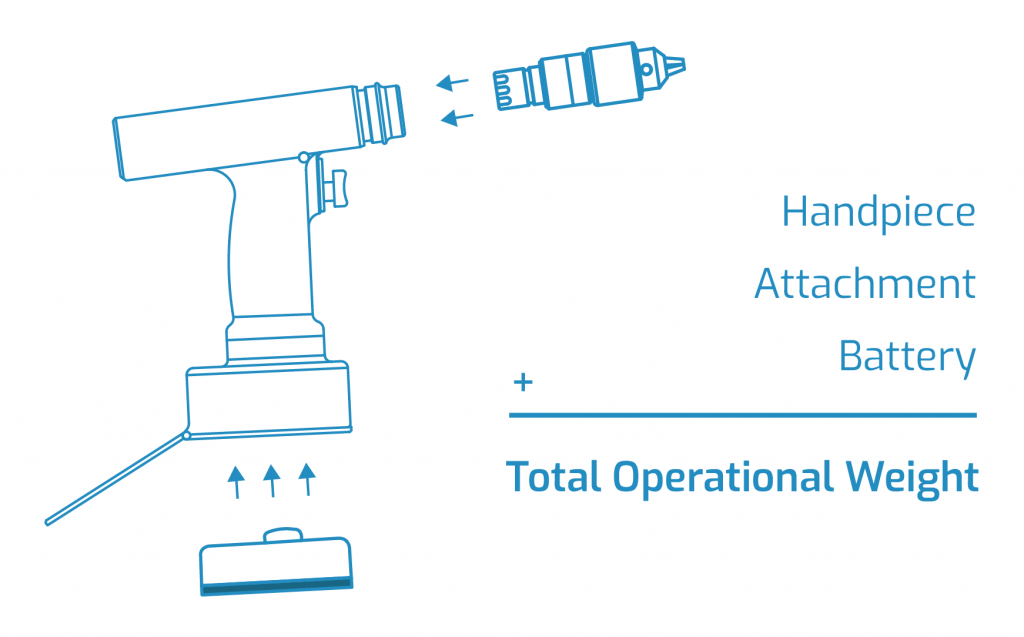
What is the sterility assurance level in surgical power tool systems? How is it ensured?
In order to ensure sterility, knowledge of the levels and types of contamination in used surgical instruments is a primary requirement. Sterility is determined by